Search Engine Optimization Service in Minneapolis
What is Search Engine Optimization?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of structuring your content and website in a way that’s friendly to search engines, with the goal of ranking high when people search online. SEO encompasses many different strategies, including keyword research, on-page SEO and search intent optimization. SEO also constantly evolves as Google and other search engines change their algorithm.
Ranking when people search on Google is essential to boost lead generation on your website. If you don’t show up within the first two pages of a Google search, your chances of getting found drop to nearly zero. It’s important not just to show up for your business name, but also for searches for what your company does.
How Does SEO Work?
This seemingly simple question has a complex answer. The easiest way to understand SEO is to start with the goal of search engines: to provide the most accurate, useful and relevant content to searchers. The criteria that search engines use to determine what is accurate, useful and relevant is their algorithm. Generally speaking, most algorithms look at the same questions:
- Does this content answer the question of the search query?
- Does the content on the page match the title of the page?
- Is the content organized in a way that’s easy to scan?
- Is the content itself clear and easy to understand?
- Are there images on the page?
- How long is the content?
- How recently was the content updated?
- How reputable is the site where this content lives?
- How much activity does this website have on a monthly basis?
- Is this website regularly updated?
- Is this site optimized for search engines?
These questions help you to understand what factors search engines take into consideration when ranking websites, but addressing them is another matter. That’s where you get into more concrete strategies: keyword research, on-page and off-page SEO, search intent optimization, voice search and local SEO.
Want to Improve Your Site’s On-Page SEO?
If you are new to SEO, you may want to start with the basics. Download our SEO Checklist to see which on-page elements you can optimize to rank higher in search engines.
What are Keywords and What is Keyword Research?
A keyword is a word or phrase you type or speak into Google. Examples include “florists near me” or “what is SEO?” Keywords are important to SEO because they help search engines identify what a specific page or blog is about. Before continuing on the other steps of SEO, it’s important to identify what keyword(s) are the main focus of each page of content on your website. There are two primary types of keywords: short tail and long tail keywords. Short tail keywords are only one or two words, while long tail keywords are longer phrases.
Example:
Short Tail Keyword: SEO
Long Tail Keyword: What is On-Page SEO?
Both types of keywords are important to consider when building content. However, if you want to compete online long tail keywords are typically a better strategy. Short tail keywords are so vague and used on so many websites that it’s nearly impossible in most cases to rank on the first page for them. However, long tail keywords are much more specific and varied, meaning that there are less pages online about the same exact subject matter.
Keyword research is the starting point for all SEO strategies. It is the process of finding and researching what terms people enter into Google to choose the best keywords.
Step 1: Start Broad
If you’re building a keyword strategy for your website as a whole, you’ll want to start broad and then narrow in. Start with a list of the top 5-10 generic keywords that describe your business. These will likely be your services or product offerings, and likely be short tail as well. HubSpot describes these keywords as a “bucket” that will house other, more specific keywords.
Step 2: Use Tools to Get Specific
Once you’ve identified your high-level keywords, this is where the “research” portion of keyword research comes into play. You’ll want to look at the phrases that people type into Google that are related to your high-level keywords in order to create long tail keywords. First, there’s Google Trends. This tool will not only show you how many people search for a keyword, but it will also suggest related keywords. This can be very helpful when you’re trying to think of specific keywords or turn short tail keywords into longer phrases. Next, use Google’s Keyword Planner. This tool will show you how much traffic each keyword receives each month, how much it will cost if you want to advertise using that keyword, as well as a rough idea about how competitive the keyword is. This can help you decide which short tail and long tail keywords you want to pursue for the best chance of increasing your rankings.
You can also use tools like SEMrush and Keywords Everywhere to find suggested long tail keywords. However, it can be challenging to find the right keywords – you may find that the ones you want to go after have no search volume. This is where an SEO expert can help you identify strategic keywords that strike a balance between being relevant and having a decent search volume.
Once you’ve identified your main keywords for both your site and the specific pages, you can begin the core of all SEO: on-page SEO.
How’s Your Digital Marketing Strategy?

What is On-Page SEO?
Simply put, on-page SEO is the practice of optimizing your website content and HTML to best rank in search engines. This means defining what your page is about, as well as organizing each element so that search engines can read it. This includes your page title, URL, content, meta title, meta description, alt tags, links and headings. If the prospect of diving into your HTML makes you dizzy, don’t panic. Luckily, most modern content platforms like WordPress and HubSpot have sections where you can directly enter in that information instead of having to go into the actual code of your page.
On-Page SEO Key Factors
When performing on-page SEO, it’s most helpful to follow a checklist to make sure you’re not missing anything. For more information on this checklist, check out our blog post: On-Page SEO Steps [Free Checklist].
Definitions of SEO Terms
Page/Meta Title
The title is the single most important element when it comes to ranking. Your title should convey the meaning of your content and ideally include a keyword. Your title could either include a short tail keyword or long tail keyword. Here’s an example of how that could break down:
Short tail keyword: “digital marketing”
Page Meta Title: “Digital Marketing | BizzyWeb”
Long tail keyword: “digital marketing examples”
Blog Meta Title: “8 Digital Marketing Examples You’ll Want to Try”
Meta Description
The meta description is the small preview of text that appears underneath your search result. In past years, the meta description held more weight. While it’s still important, it’s not as critical as the title or actual content of your page. Ideally, your meta description should include your keyword and be a short summary of your content. If your goal is to get a featured snippet or rank for voice search, it helps to have a question/answer format for your meta title and meta description.
Example:
Meta Title: “Does Medicare Cover a Gym Membership?”
Meta Description: Medicare does not cover fitness programs and gym memberships, but private health plans may offer gym memberships.
Page URL
The URL for your page is also key for SEO, since Google is very conscious of bait-and-switch content and will try and shut it down. Your URL should match with your page title, but you may need to trim it down to avoid excessive length, redundancy or misleading content. For example:
Page Title: “Digital Marketing | BizzyWeb”
Do This: https//www.bizzyweb.com/digital-marketing
Not This: https://www.bizzyweb.com/digital-marketing-bizzyweb
Never This: https://www.bizzyweb.com/digital-marketing-tips-and-tricks
In the last example, the URL is misleading because the page does not share tips and tricks. Your URL should match your content.
Alt Tags
An Alt Tag, also known as an Alt Attribute or Alt Description, is a description applied to image tags to provide a text alternative for search engines. Since a search engine algorithm can’t “read” an image, we need to give some words so the algorithm can “read” the image and know what it is. This gives relativity between the content and image for the search engines. If appropriate, you can include relevant keywords in your alt tags. You do not need to begin your alt tag with “an image of…” or “a picture of…” – search engines and screen readers alike will provide that information to the end user.
Example:
Image:

Alt text: “A brown puppy jumping”
Subheadings
It’s useful to break up content with subheadings for readability, but these also are important for your SEO. Your subheadings should be formatting as H2 and your sub-subheadings as H3 – you will see these options in your website content editing program. Subheadings should be used to dictate various sections of content.
Example:
Page Title: The Complete Guide to SEO
Example Subheadings:
- What is Search Engine Optimization?
- What is On-Page SEO?
- What’s the Difference Between SEO & PPC?
Internal and External Links
It also improves your overall SEO to include links in the body of your content to relevant content, where appropriate. For example, in a blog post about bathroom remodeling trends, you should include a link to your bathroom remodeling page. Internal links are any links on your website to other areas of your website, while external links are links to other websites. While it may seem like linking away from your website would be bad for SEO, it’s actually the opposite – search engines consider external links in their rankings. A good rule of thumb is to set any external link to open in a new window. That way, your site still remains open for the user.
Body Content
The body of your blog or page simply refers to the actual meat of your content – not just the headings, subheadings, images, etc., but the words on the page. Creating compelling content is a separate skill onto itself, but for SEO purposes it’s critical to ensure that the content on your page matches the title of the page. That may sound obvious, but it’s very easy to stray away from your topic once you begin actually writing. For more tips on how to write content that search engines love, check out our blog: How to Create SEO Content.
What is Off-Page SEO?
So far we’ve discussed how to improve SEO on your own website. However, there is another component to SEO that happens off of your website. Off-page SEO is everything that you or others do away from your website to drive traffic back to your site. The most common off-page SEO strategies are:
- Linking back to your site on your own social media posts
- Linking back to your website on your marketing emails
- Updating your Google My Business listing
- Updating your listing on other directories, such as Yelp, Angie’s List, etc.
- Other websites linking to your website
- Guest blogging
- Influencer marketing
- Online advertising
All of your off-page SEO strategies support the work you do on-page by promoting your website to new viewers.
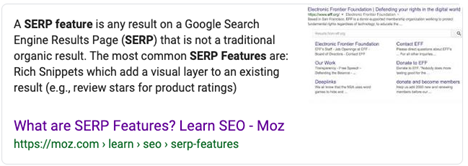
What are SERP and Featured Snippets?

SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page and refers to the page a user sees or hears after they ask a search query. The standard format for a search result listing is the page URL, followed by the page title and then the meta description. As search engines have evolved, the SERP page has evolved to include other media elements and features.
The most common SERP feature you’ll see are featured snippets. Featured snippets answer a search query directly within Google. They are typically very short and to the point.
This allows users to answer their question without ever needing to leave Google, although many users will still click on the link to learn more about a given topic. Google hasn’t revealed exactly what criteria they use when selecting which result will be given a featured snippet, however it’s always a result from the first page of SERP. This means that SEO is critical for trying to snag a featured snippet.
Read Now: What are SERP Features? And Why Do They Matter?
Is Your Website Search Engine Optimized?
Our free Buzz Report scans your website for on-page SEO, site speed and other key SEO factors to deliver a score from 1-100. You’ll know how search engines see your website and get a detailed breakdown of every element that needs to be improved.
What is Search Intent Optimization?
How often has this happened to you: you search for a recipe online, click on one of the first results you see in Google… only to be met with a massive wall of text and photos?
This exact situation is where search intent and search engine optimization (SEO) clash. Your intent was to find a simple recipe, but what you got instead was a page that was optimized for Google. Ranking on Google is important, but it’s just as important to keep people on your page once they click on your link. That’s where search intent optimization comes in. It’s choosing keywords and optimizing your content with your user’s intent in mind.
The Types of Search Intent
Informational intent are searches based on gathering information, both basic and complex. It could be information on the weather, how to grow vegetables, or SEO tips (like this page!). In this type of search, people have a specific question or want to know more about a certain topic.
Navigational intent are searches to get to a certain website. For example, searching “Facebook” into Google, to try and get to Facebook. Generally speaking, you will rank high for your business’ name by default.
Transactional intent are searches based on retail or eCommerce. These are searches with the intent to buy a specific product, like “high waisted jeans” or “cheap sunglasses.”
Commercial intent are searches for future purchases. People may know they need a larger item in the future and want to do research online before making a purchasing decision. This could be a washing machine, a business service, etc. Think of this category as a combination of informational and transactional intent.
Keyword intent are searches that use specific words that clue you into their intent. Things like “buy, deal, discount” let you know that they want to purchase. Things like “how to, best way to” let you know they want information. This type of intent usually overlaps with one of the other four intents.
Knowing the intent behind a search can help you find the best possible keywords to use and also give guidance on how to set up a page. For more information about search intent optimization, check out our blog post:
Read Now: Why Search Intent Optimization is as Important as SEO.
What is Voice Search?
Voice search is when people use devices like their smartphones, Alexa, Google Home, Amazon Echo, etc. to ask questions. This differs from traditional search in that phrases are usually longer or more conversational. On a computer, you might type in “sushi restaurants” but on a phone you might say: Hey Siri, what’s the best sushi restaurant near me?
You may want to optimize your website for voice search to capture that traffic. For more information voice search SEO, check out our blog post: How Do I Optimize My Website for Voice Search?
What is Local SEO?
Local search is the strategy and practice of attracting local business and customers online. It’s very important for any retail, service, or manufacturing entity that doesn’t exist solely online. This includes choosing keywords that include your physical location (ex. Minneapolis digital marketing), as well as other targeted strategies. Local SEO is most important for any business that has a physical location or primarily serves customers in specific geographical regions. It’s also a popular strategy because it’s typically easier to compete on a local level than it is on a national level for short tail keywords.
What’s the Difference Between SEO & PPC?
Sometimes, the terms SEO and PPC are mentioned together. While similar, they are different. PPC advertising, or pay per click, is an online marketing tool based around ads. Two of the most popular platforms for PPC ads are Facebook and Google. Unlike SEO, you have to pay each time someone clicks on the ad. Online advertising on Google is also separate from what’s called organic SEO – all of the SEO strategies we’ve been covering so far on this page. When searching on Google, there’s a clear distinction between the online ads (PPC) and the rest of the search results (Organic SEO). You can see this in action when you search on Google:
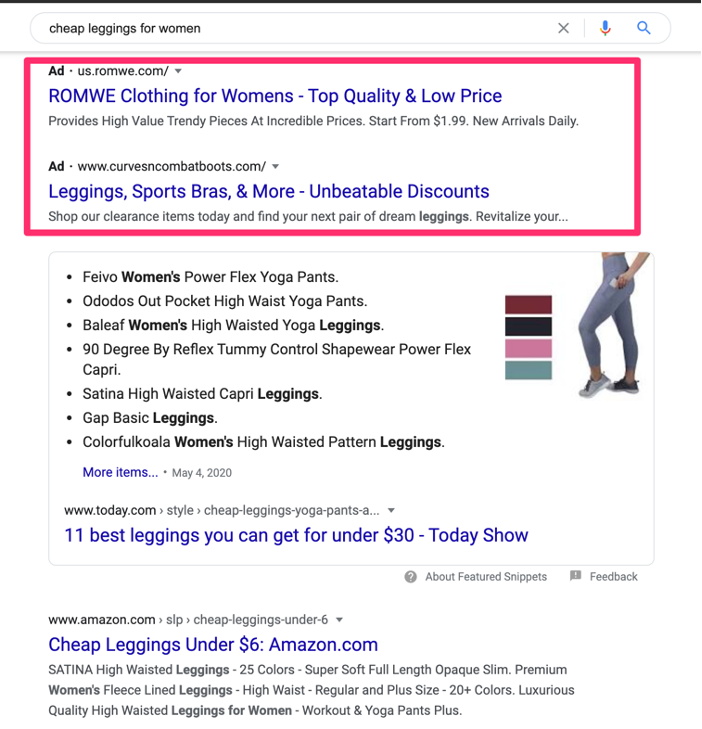
The first search results are all ads and are marked with a clear “Ad” at the start of the text. The organic search results, seen below, are not marked as ads.

BizzyWeb SEO Services
BizzyWeb is a full-service Digital Marketing, Inbound Marketing and Growth-Driven Web Design agency, based in Minneapolis. We offer SEO services as part of our Digital Marketing and Inbound Marketing programs for supercharging growth.
Our team members are HubSpot, WordPress, Google and Constant Contact certified, and we’re leading partners with each. With HubSpot, we’re Diamond Tier Partners, which puts us in the top 1% of partners worldwide.



